Welcome to the scikit-package official documentation!
scikit-package offers tools and practices for the scientific community to make better and more reusable Scientific Python packages and applications.
How to cite scikit-package
If you use scikit-package to standardize your Python software, we would like you to cite scikit-package:
Lee and C. Myers and A. Yang and T. Zhang and S. J. L. Billinge, scikit-package - software packaging standards and roadmap for sharing reproducible scientific software (https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.03328)
How does scikit-package benefit scientists?
scikit-package offers step-by-step instructions for reusing and sharing code, starting from something as simple as defining and using functions, all the way to maintaining and releasing a fully documented open-source package on PyPI and conda-forge.
Here are the 3 goals of scikit-package for the scientific community:
We help scientists share scientific code to amplify research impact.
We help scientists save time, allowing them to focus on writing scientific code.
We offer best practices from the Billinge group’s experience in developing scientific software.
Here is an overview of the five levels of reusing and sharing code and the key features of scikit-package:
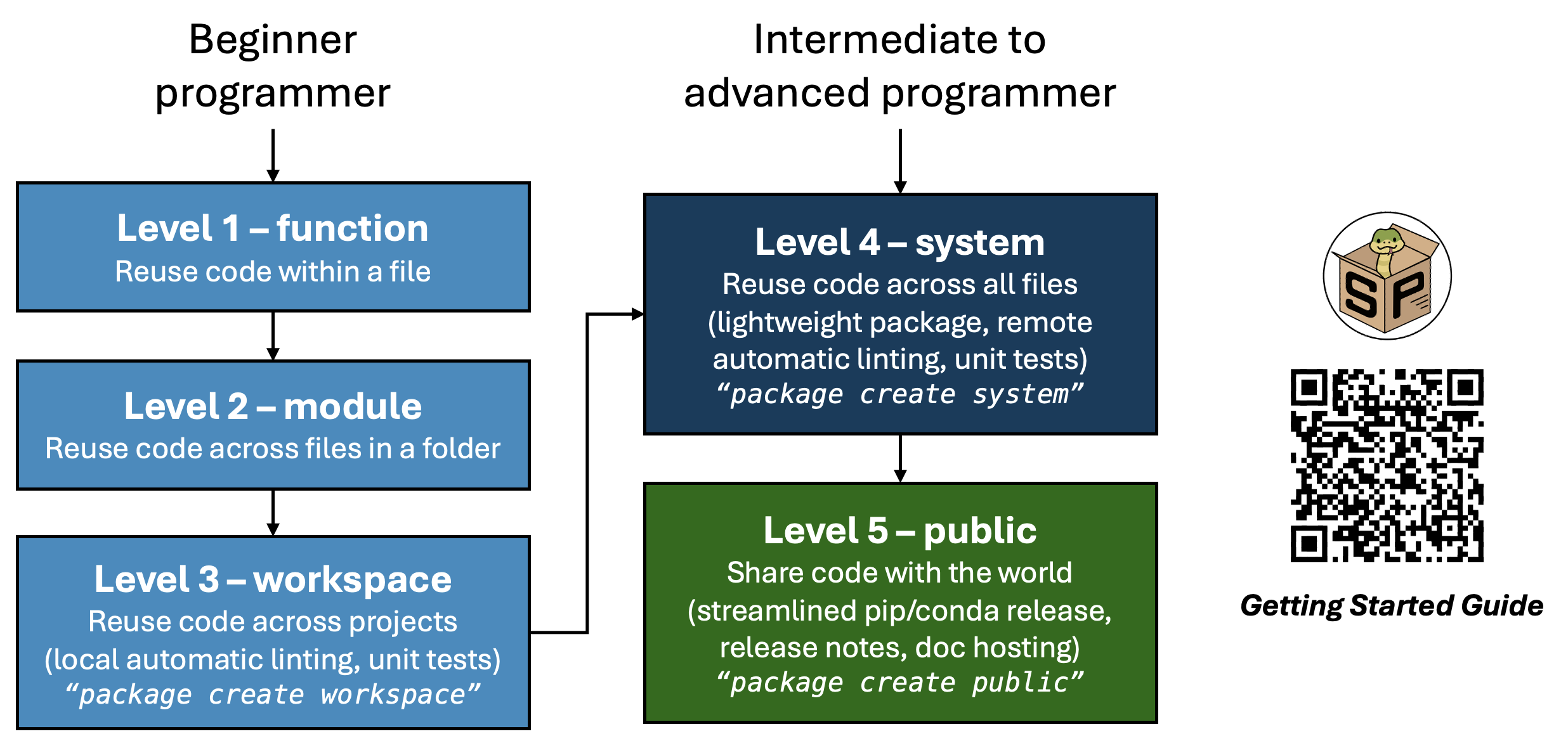
The steps are divided into five levels of shareability and complexity, allowing users to choose the level that best suits their current needs. Code can be moved to higher levels as necessary.
Level 1,
function, which is already widely used, consists of simply defining functions within the same file or module.Level 2,
module, expands on Level 1 by reusing functions across separate module files within the same directory.Level 3,
workspace, restructures the organization so that a block of code can be reused across multiple projects.Level 4,
system, enables users to create a lightweight package so that the code can be reused across all files locally.Level 5,
public, is the final step, where the source code is uploaded online so that anyone in the world can install the package, sourced from PyPI or conda-forge.
Who is using scikit-package?
The full list of packages is as follows:
How do I get started?
Please visit the Overview page to learn how to navigate the documentation!
Demo
Here is how you can use the package create public command to create a new Level 5 Python package called diffpy.my-project in just 1–2 minutes:
Of course, you can start a lightweight package (Level 4) using the package create system command.
What are the full benefits when I reach Level 5?
Streamline the release process by pushing a Git tag to trigger a sequence of actions: publishing to PyPI and GitHub, updating hosted documentation, and updating the
CHANGELOG.rstfile. Visit Publish on GitHub and to PyPI for more details.Host documentation with a public URL using a
Sphinxtemplate as part of the PyPI and GitHub release. Includes live rendering, API documentation, and previews for each pull request.Set custom default metadata such as authors, project description, license holders, and keywords when creating a new package. Automatically store and reuse the entered metadata to update your package with the latest version of the
scikit-packagestandards. To learn more, read How can I change the default values that appear in the prompt when creating projects in Level 3,4,5?.Support namespace package imports (e.g.,
import <org-name>.<package-name>) to maintain branding consistency and avoid name collisions. To learn more, read I read scikit-package allows namespace support for importing packages. What is it, and how do I set it up?.
We have also adopted community software and standards in scikit-package:
Set up both local and remote
pre-commithooks to automate linting of code. This includes checks for PEP8, PEP 256, and static files such as.json,.yml, and.md. Spelling checks are included as well. To learn more about the hooks provided at each level, read How is pre-commit used in each Level?.Provide a rich
README.rsttemplate that includes badges, installation instructions, support contacts, and contribution guidelines for your GitHub repository.Run
pytestwith the latest Python versions, adhering to the SPEC0 specification, without requiring manual configuration.
For technical users, here are some of the advanced features:
Streamline conda package release by updating
meta.yamlwithpackage create conda-forgeafter the PyPI and GitHub release. To learn more, read Create conda package with conda-forge.Support headless GitHub CI testing for GUI applications.
Support non-pure Python package releases with
cibuildwheel.Reusable GitHub Actions workflows located in scikit-package/release-scripts.
How do I receive support?
If you have any questions or have trouble, please read the Frequently asked questions (FAQ) section to see if your questions have already been answered. If there aren’t answers available, please create GitHub Issues.
How can I contribute to scikit-package?
Do you have any new features? Please make an issue via the GitHub issue tracker for further discussions. For a minor typo or grammatically incorrect sentence, please make a pull request. Before making a PR, please run pre-commit run --all-files to ensure the code is formatted.
Acknowledgements
The Billinge Group’s scikit-package has been modified from the NSLS-II scientific cookiecutter: https://github.com/nsls-ii/scientific-python-cookiecutter